Today, Bitcoin market gains mainstream attention, raising questions on sustainability.
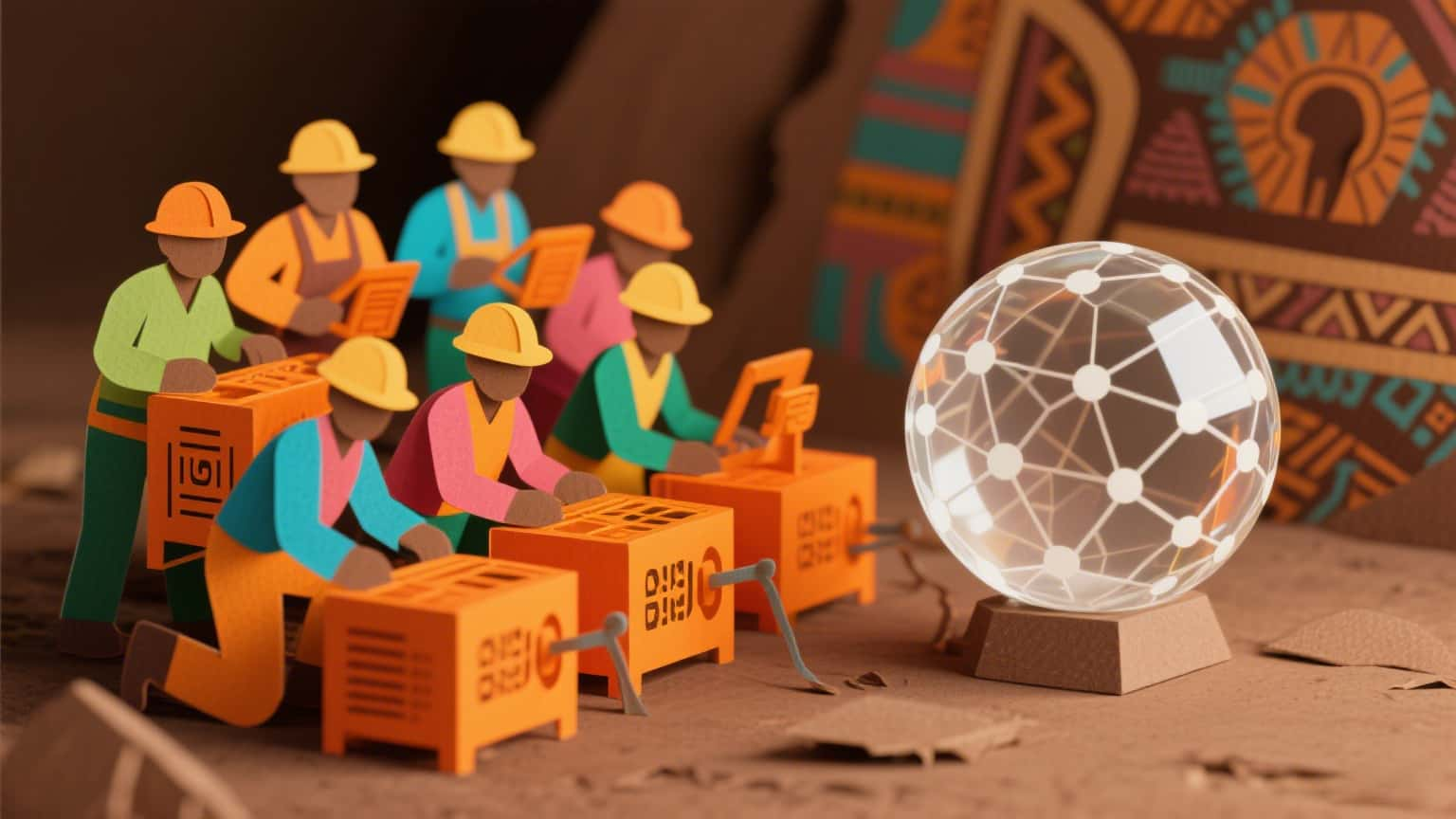

Today, Bitcoin market gains mainstream attention, raising questions on sustainability. The digital currency has been making headlines for years, but its recent surge in popularity has sparked a wave of debate. As more individuals and institutions embrace Bitcoin, the industry is facing scrutiny over its environmental impact and long-term viability.
In the past, Bitcoin was often seen as a niche investment for tech enthusiasts and libertarians. However, its market value has skyrocketed in recent years, drawing the attention of mainstream investors and media outlets. This shift has brought with it a flood of questions about the cryptocurrency&039;s sustainability. Critics argue that Bitcoin&039;s energy consumption is unsustainable, with mining operations consuming vast amounts of electricity.
To understand the sustainability issue, one must first grasp how Bitcoin works. The process of mining involves solving complex mathematical puzzles to validate transactions and create new units of the currency. This requires powerful computers to run 24/7, leading to high energy consumption. According to a report by Cambridge University, Bitcoin&039;s energy consumption is comparable to that of some small countries.
The environmental impact of this energy usage cannot be ignored. While some mining operations use renewable energy sources like hydroelectric power, many rely on fossil fuels, contributing to carbon emissions and climate change. This has led to calls for more sustainable alternatives within the industry.
Enter projects like "green" Bitcoin mining initiatives that aim to reduce the carbon footprint of cryptocurrency operations. Companies are exploring ways to integrate renewable energy sources into their mining operations, such as using solar or wind power. These efforts are crucial if Bitcoin is to maintain its growing popularity without compromising environmental integrity.
Moreover, regulatory bodies are beginning to take notice of these sustainability concerns. In some regions, governments are considering regulations that could impact how Bitcoin is mined and used. For instance, China recently banned cryptocurrency mining within its borders due to environmental concerns.
The sustainability debate around Bitcoin also raises questions about its long-term viability as an asset class. While many see it as a store of value similar to gold, others argue that its high volatility and environmental impact make it less attractive for long-term investment.
In conclusion, as Bitcoin continues to gain mainstream attention, the industry must address its sustainability challenges head-on. Whether through technological innovation or regulatory changes, finding solutions will be key to ensuring that this digital currency can thrive without harming our planet.
The path forward for Bitcoin is not without obstacles, but with increasing awareness and action from both within and outside the industry, there is hope for a more sustainable future for this groundbreaking technology.

 繁體中文
繁體中文 简体中文
简体中文 日本語
日本語 한국어
한국어 Español
Español Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch Italiano
Italiano Русский
Русский Português
Português العربية
العربية Türkçe
Türkçe ภาษาไทย
ภาษาไทย हिंदी
हिंदी Bahasa Indonesia
Bahasa Indonesia Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt




